
Light Waves Background Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
The amplitude of an electromagnetic wave is related to the strength of the electric and magnetic fields causing the wave. All light travels at the same speed, but each color has a different wavelength and frequency. Amplitude and wavelength are shown in Figure 2.1. Figure 2.1: Waves are described by several properties, two of which are shown here.
.jpg)
Can It Be Saturday Now ? Light wave
The interference pattern produced from a single wavelength of light on the sensor screen is evidence that light is a wave. Thomas Young found this in 1801 when he first carried out his.

Light wave technique an advance for optical research RMIT University
It's not as odd as it might seem, either. Particles and waves are sometimes conceived as opposites, but they're not. Also, light is not the only thing that exhibits behavior of both particles and waves. Other quantum entities also have this behavioral duality, and wave-particle duality is a key focus of the study of quantum mechanics.

Slow Shutter Light Waves Design 698757 Vector Art at Vecteezy
The wave equation included physical constants from both electricity and magnetism, and extracting the wave speed from this equation resulted in a number Maxwell was already familiar with - the speed of light. It is traditional to denote this speed with a lower-case 'c': (3.1.1) c = 3.0 × 10 8 m s. So the "displacement" of such a wave is.
PPT BEHAVIORS OF WAVES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5057227
In a nutshell: The color we percieve an object to have, is the light that was reflected by that object. For example, a (yellow) banana is reflecting light of approximately 580 nm wavelength. It absorbs the rest (or at least the rest of the visible wavelengths). So the color we see is the light that is reflected.

Light, sound, action extending the life of acoustic waves on microchips The University of Sydney
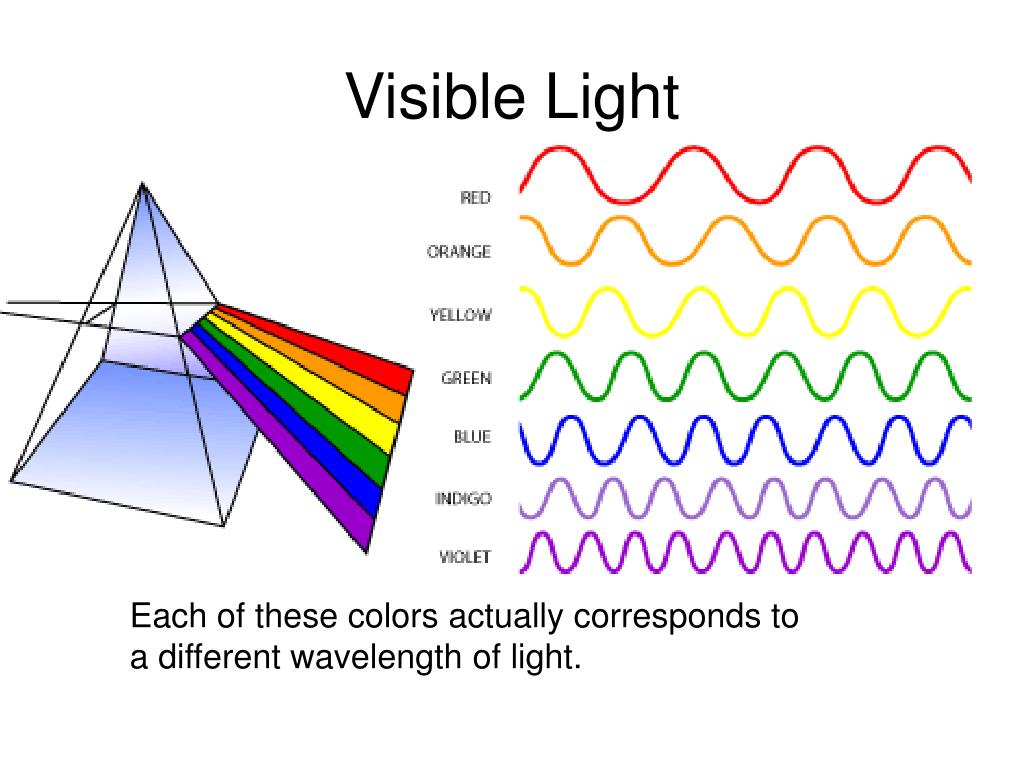
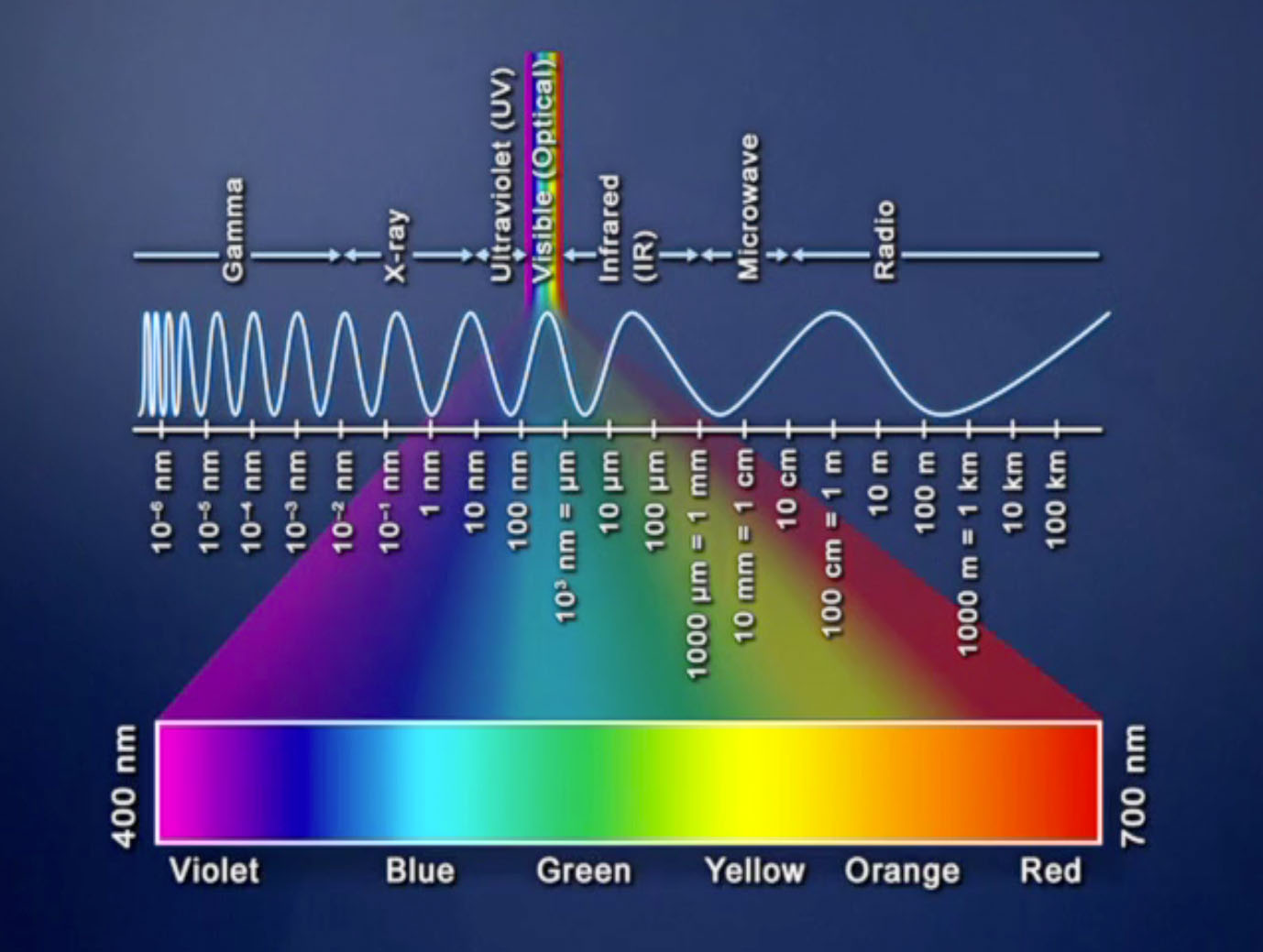
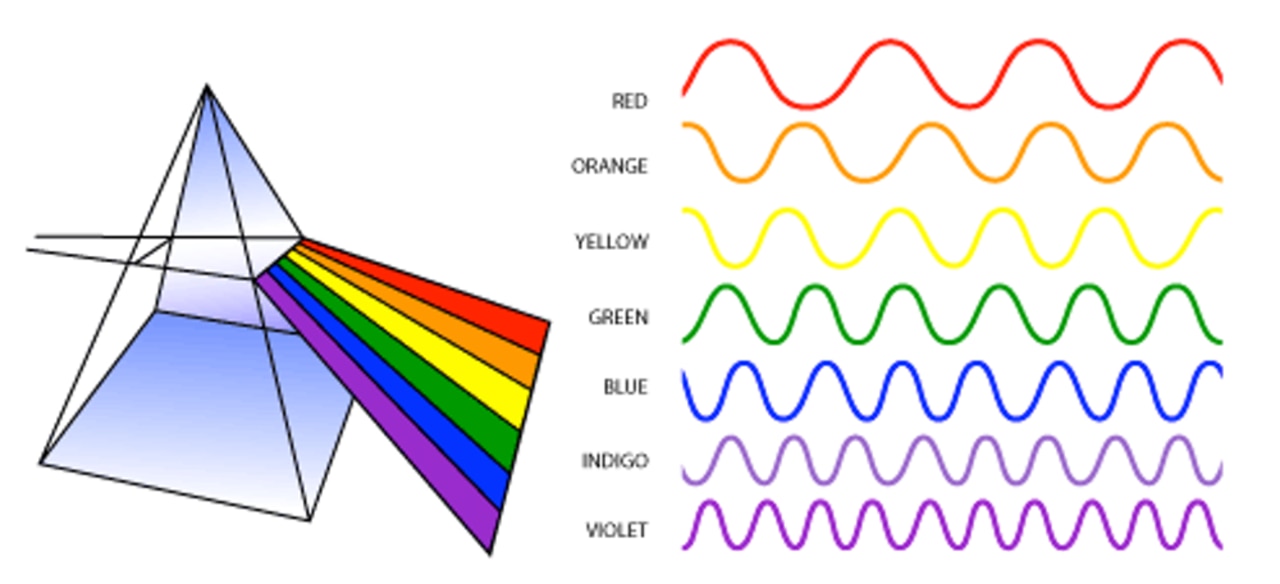
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. [1] Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400-700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750-420 terahertz, between the infrared (with longer wavelengths) and the ultraviolet (with shorter wavelengths). [2] [3]

How do waves wave? Physics Stack Exchange
1.1: The Wave Nature of Light. to learn about the characteristics of electromagnetic waves. Light, X-Rays, infrared and microwaves among the types of electromagnetic waves. Scientists discovered much of what we know about the structure of the atom by observing the interaction of atoms with various forms of radiant, or transmitted, energy, such.

The Spectrum Digicloud
light, electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation occurs over an extremely wide range of wavelengths, from gamma rays with wavelengths less than about 1 × 10 −11 metre to radio waves measured in metres.

Light Waves Stock Animation 203819
c = λ ν where λ (the Greek lambda) is the wavelength (in meters, m ) and ν (the Greek nu) is the frequency (in Hertz, Hz ). Their product is the constant c , the speed of light, which is equal to 3.00 × 10 8 m/s .
The Vedic Wisdom The knowledge of unknown Light Wavelength Info
Wave-particle duality is the concept in quantum mechanics that quantum entities exhibit particle or wave properties according to the experimental circumstances.: 59 It expresses the inability of the classical concepts such as particle or wave to fully describe the behavior of quantum objects.: III:1-1 During the 19th and early 20th centuries, light was found to behave as a wave, and then.

Free Stock Photo 3572light waves freeimageslive
Baby Loss Awareness Week culminates with the global "Wave of Light" on 15th October, which is also a globally recognised event. We invite you to join other families across the world by lighting a candle at 7pm local time and leaving it burning for at least one hour to remember all babies that have died too soon.

The first ever photograph of light as a particle and a wave EurekAlert! Science News
Light waves across the electromagnetic spectrum behave in similar ways. When a light wave encounters an object, they are either transmitted, reflected, absorbed, refracted, polarized, diffracted, or scattered depending on the composition of the object and the wavelength of the light. Specialized instruments onboard NASA spacecraft and airplanes collect data on how electromagnetic waves behave
/light-pattern--artwork-724234931-5c55f10846e0fb000164d999.jpg)
WaveParticle Duality Definition
Physicists describe light as both a particle and a wave. In fact, light's wavelike behavior is responsible for a lot of its cool effects, such as the iridescent colors produced on the surface of.
/GettyImages-1163082272-086b7391595642ab9378cb3115219792.jpg)
Visible Light Definition and Wavelengths
The visible light spectrum is the segment of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can view. More simply, this range of wavelengths is called visible light. Typically, the human eye can detect wavelengths from 380 to 700 nanometers. WAVELENGTHS OF VISIBLE LIGHT

Light Waves 09 Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
Light is a transverse, electromagnetic wave that can be seen by the typical human. The wave nature of light was first illustrated through experiments on diffraction and interference. Like all electromagnetic waves, light can travel through a vacuum. The transverse nature of light can be demonstrated through polarization.
Explainer answering the common question why is the sky blue? KidsNews
The wavelength of light is defined as "The distance between the two successive crests or troughs of the light wave". It is denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Therefore, the distance between either one crest or trough of one wave and the next wave is known as wavelength. What Is Visible Spectrum?